Context and goal
Policy support for a wide-scale deployment of Energy Smart Appliances is a complex matter, crossing the fields of product and digital-related policy instruments. Any potential measure would not directly address energy efficiency, but instead will essentially seek to certify a specific ‘energy-smart’ behavior of products.
This initiative, led by DG ENER and the Joint Research Centre, aims to propose a Code of Conduct (CoC) to the Energy Smart Appliances (ESA) manufacturers for adherence. The version 1.0 of the CoC for ESA is final, please, click here to download.
The design of the CoC addresses two main challenges:
• The definition of the principles for data sharing among appliances, home & residential building automation systems, EV chargers, aggregators, DSOs
• The development of Interoperability requirements for ESA Stakeholders (industry, NGOs, academia) and Member States authorities will be involved in this process Involvement and communication with stakeholders will be undertaken in a combination of questionnaires, webinars and physical meetings. The coordination of stakeholders will be carried out jointly by DG ENER and the JRC.
Please contact us via email JRC-ENERGY-SMART-APPLIANCES@ec.europa.eu to follow the developments of the project and be part of the co-design of the CoC.
Code of Conduct Phase 2
The Second phase of this initiative of developing a Code of Conduct for Energy Smart Appliances promotes the cooperation with the stakeholders trough 2 working groups:
- Process working group
- Technical working group
Members have participated in a couple of meetings and a dedicated collaborative space has been missed en place
Workshops- Phase 2
Workshop Kick-off Second Phase (18 September 2024)
The workshop on Energy Management Interoperability of Energy Smart Appliances took place on September 18th, 2024, in Brussels, Belgium, as the kick-off of the second phase of the Code of Conduct (CoC) project, which aims to develop a common framework for the interoperability of energy smart appliances.
Workshop Topics:
- Introduce the second phase of the CoC project and its objectives
- Present the results of the survey on Energy Management Systems (EMS) and their interaction with Energy Smart Appliances (ESA)
- Discuss the expansion of the CoC to include new devices, such as energy management systems (EMS), photovoltaic inverters (PVI), and electrical vehicle chargers (EVC)
- Explore the possibility of updating the first version of the CoC to include new solutions and protocols
The workshop featured presentations, discussions, and networking opportunities with stakeholders from the energy management industry.
Agenda and presentations:
- Final Agenda - CoC Phase 2 - First Workshop - 18 SEP 2024
- 1.2. Overview of the CoC v.1.0 - Accomplishments and Challenges – DG ENER
- 1.3. Energy Services in EMS & Semantic Interoperability – DG JRC
- 1.4. Timeline of the Second Phase – DG ENER
- 1.5. Energy Management System (EMS) Survey Results – DG JRC
- 2.3 DLMS - Linking SDOs to CoC - Sergio Lazzarotto
- 3.2 CSA - Mapping new example to SAREF in Annex 3 CoC v.1.0 - James Harrow
- 3.2 HCA - Mapping new example to SAREF in Annex 3 CoC v.1.0 - Michael Siemann
- 3.3 ETSI - SAREF European Norm (EN) - Joachim Koss
- 3.4 S2 Standard - New Use Case - Mente Konsman
- 4.1 Trialog - IOP Standards & CoC Ontology Tester - Antonio Kung
Code of Conduct v.1.0
The Version 1.0 of the Code of Conduct for Energy Smart Appliance is final, please, click here to download.
We are glad to announce the first 11 manufacturers who have signed, here below:

GEO
Furthermore, a Home Energy Management System manufacturer, geo, have committed to support compliant appliances.
Workshops for CoC v.1.0
Launch event (23 April 2024)
The launch event took place during the EU Energy Day at the Hannover Fair on 23 April.
You will find the press release issued for the event here. You can also download the photos of the session from this folder that contains photos from all panel sessions of the day.
The draft of methodology report on smart appliances is out. Please click here
Workshop 3 (23 June 2023)
A final version of the CoC and the foundation of the testing methodology were exposed.
Presentations:
Workshop 2 (24 March 2023)
In this Workshop the first draft of the CoC was presented and discussed with the stakeholders.
Presentations and documentation:
- WS2.1.Result of the survey launched with the contribution from the stakeholders.
- WS2.1.First draft of the European Code of Conduct for Interoperability of Energy Smart Appliances
Workshop 1 (8 November 2022)
The results of a previous survey about interoperability of ESA and the report about the Analysis on Data Exchange from State-of-the-art Use Cases regarding Energy Smart Appliances’ Interoperability.
Presentations and documentation:
- WS1.1.Welcome address by Head of Unit from JRC.C.3 Energy Security, Distribution and Markets
- WS1.2.Opening of the Workshop from DG ENER
- WS1.3.Presentation of Technical Report on ESA interoperability from JRC
- WS1.4.Presentation of the results of the ESA interoperability Survey from JRC
- WS1.5.Minutes of the Workshop
Development Steps for the first release
Under the ecodesign & energy labelling framework, some preparatory work for addressing ESA has been completed. The preparatory study[1] established the scope for further work (i.e. selected product categories with the highest potential for demand response), validated the economic benefits that can be achieved by a large scale deployment of ESA, and proposed some generic technical requirements for those. As a general approach, the study proposed a non-mandatory measure (i.e. to help differentiate on the market the ESA and ensure their full interoperability, but not to ban ‘non-smart’ products from the market). However, the study’s conclusion is that more work is needed in order to come up with a regulatory proposal.
The main issue identified is regulating in a way that would ensure full interoperability among different products from various manufacturers. This would require compliance with a multitude of standards, some of them not yet (fully) developed. In addition, any such regulation would heavily rely on these standards (references to which might need to be included in the regulatory text), while the standards themselves are in a very rapid evolution (much faster than the regulatory cycles).
Thus, while regulation seems inappropriate, rapid technological developments could also lead to the consolidation of different product ecosystems, which will use proprietary solutions and will inherently be incompatible (i.e. not interoperable) with each other. Therefore, action could be taken by the European Commission for securing coherent development on the market, adherence of industry to open standards, and promotion of Smart Applications REFerence (SAREF) as a general ontology[2] underpinning product interoperability.

The work should build on the activities
The work should build on the activities of the newly started InterConnect project, funded under Horizon 2020. Many relevant stakeholders are project partners, and the project itself intends to demonstrate (and develop/extend) the use of SAREF for ensuring interoperability for demand side flexibility. Thus, a natural continuation would consist of: i) developing the CoC, and ii) ensuring the adherence of a sufficient number of signatories, with enough market coverage in their fields.
Stakeholders (industry, NGOs, academia) and Member States authorities will be involved in the process at different stages do discuss draft documents and proposals. Involvement and communication with stakeholders will be undertaken in a combination of questionnaires, webinars and physical meetings (to the extent possible in light of the COVID pandemic). The coordination of stakeholders will be carried out jointly by DG ENER and the JRC.
Workflow
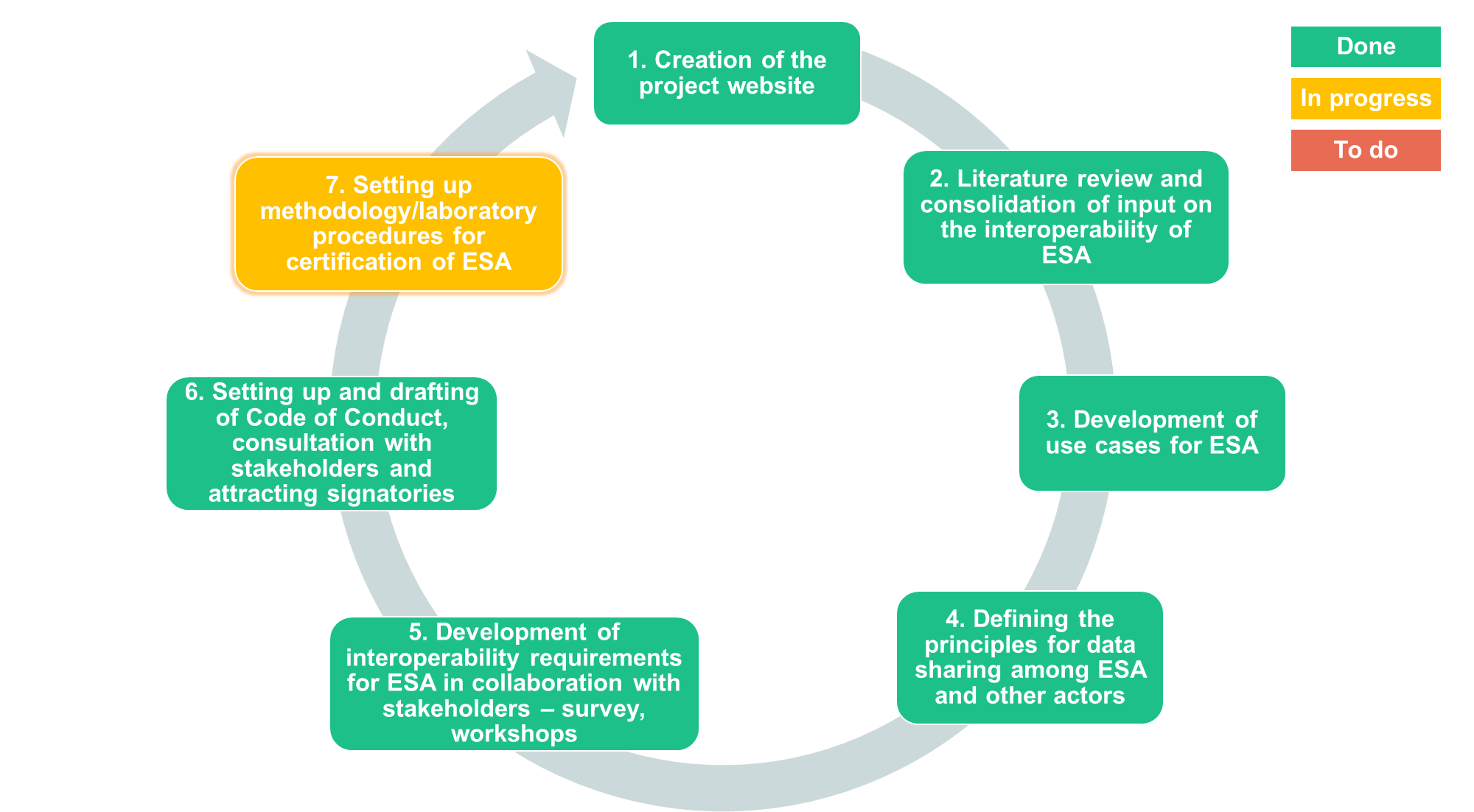
The JRC will complete and extend the work done, over a time of 24 months along the following issues and milestones:
1. Creation of project website.
2. Literature review and consolidation of input from relevant sources on the interoperability of energy smart appliances such as the InterConnect project[3], standardisation efforts in other countries or regions (i.e. UK, California, etc.).
3. Development of use cases for energy smart appliances.
4. Defining the principles for data sharing among appliances, home & building automation systems, EV chargers, aggregators, DSOs. [4]
5. Development of interoperability requirements for energy-smart appliances; in collaboration with external parties, such as manufacturers, etc.
6. Setting up a CoC; drafting the CoC, consulting the stakeholders and attracting signatories
7. Setting up methodology/laboratory procedures for the certification/conformity purposes of energy smart appliances.
The status of the project is showed in the next picture:
JRC supports:
JRC supports the discussions and decisions of the Task Force with analysis and research, resulting in input documents for each of issues above. The format and structure is reviewed by DG ENER, who supervises and leads the activity.
If appropriate and in agreement with DG ENER, particular elements of the issues (6) and/or (7) above may be outsourced to external consultants with specific expertise in this area.
Legend
[1] https://circabc.europa.eu/
[2] “Ontology = formal specification of a conceptualization, used to explicitly capture the semantics of a certain reality” (definition from the ETSI SAREF technical specification TS 103 264). In other words and ontology provides a general vocabulary that explains the data which is being exchanged and makes it comprehensible for different communication technologies that are ‘SAREF compliant’. SAREF4ENER extension was developed specifically to enable the (currently missing) interoperability among various proprietary solutions developed by different consortia in the smart home domain.
More info at https://ec.europa.eu/digital-single-market/en/news/digitalising-energy-sector-common-language-consumer-centric-world
Timetable
| Deliverables | Deadline/Timeline |
| Start of project | T0 |
| Kick-off meeting | T0+3 weeks |
| Project website | T0+ 6 weeks |
| Reports of issues 2 to 4 | T0+ 5 months |
| Report of issue 5 | T0+ 14 months |
| Report of issue 6 | T0+ 16 months |
| Report of issue 7 | T0+ 19 months |
| Final report | T0+ 21 months |
* T0= mid August 2021
Related Links & Documents

Report of issues 2-4: Energy Smart Appliances’ Interoperability: Analysis on Data Exchange from State-of-the-art Use Cases
Policy support for a wide-scale deployment of energy smart appliances seems a complex matter, crossing the fields of product and digital-related policy instruments. Any potential measure would not directly address energy efficiency, but instead will essentially seek to certify a specific ‘energy-smart’ behaviour of products.
In this project DG ENER and the Join Research Centre would propose a Code of Conduct to the energy smart appliances manufactures for adherence.

Issue 5: Survey on interoperability of Energy Smart Appliances
Energy Smart Appliances (ESA) are the instrument to transform houses/buildings into smart. They also empower consumers in becoming active players of the smart grid. However, a wide-scale deployment of ESA may induce interoperability (IOP) issues. Therefore, a concrete approach is needed to reassure that IOP is preserved in the system while ESA are introduced in the market.
