Introduction
The JRC Smart Grid Interoperability Laboratory (additional info on the EU Science Hub) is a testing facility on the interoperability of smart grid systems. It aims to assess technological implementations according to proposed standards, use cases and processes in conjunction with applicable reference architectures. Through our experimental facilities we contribute to policy making and industrial innovation regarding the modernisation of the electricity grid. The lab works on the verification of the interworks among grid components, benchmarking of different solutions, and identification of gaps and challenges. The work is performed in collaboration with industry and research institutions.
The lab allows interoperability testing of smart grid components following experimental procedures, simulations and emulations and utilising accepted standards. The assessment of interoperability is done with reference to use cases and quantitative assumptions stipulated by industry and standardization bodies. The focus is extended in identifying also the factors that could potentially compromise interoperability.
What is interoperability?
Interoperability is the ability of an equipment to be integrated in a system and exchange meaningful information, understand the exchanged information and comply with the system rules maintaining the quality of service. It is a fundamental element for the Smart Grid where a key challenge is integration affecting components, information, systems and implementations.
The Smart Grid exhibits a high complexity regarding organizational and technological aspects. Key challenge of the Smart Grid is integration, affecting components, information, systems and applications. Functionalities and interfaces should ensure interworks in order to enable high-level processes. Connecting all of the pieces in a power grid gives rise to an interconnected network in which communication and analysis will take place in real time. Information and Communication Technologies (ICT) like Machine to Machine Communicators, Agent technology and Internet of Things will enable the migration of the classical power system towards the modernisation of the grid.
Interoperability is an essential requirement for this migration process and should be carefully considered since any operational, architectural and functional failure will have high cost due to the scale of the power system and its economy. Moreover, interoperability is crucial for deploying Smart Grids open to all vendors and integrators, where the operators can concentrate on the top-level functions, independent from proprietary solutions. Hence, interoperability is at the same time a technical imperative, and the enabler of an open market where innovation can flourish.
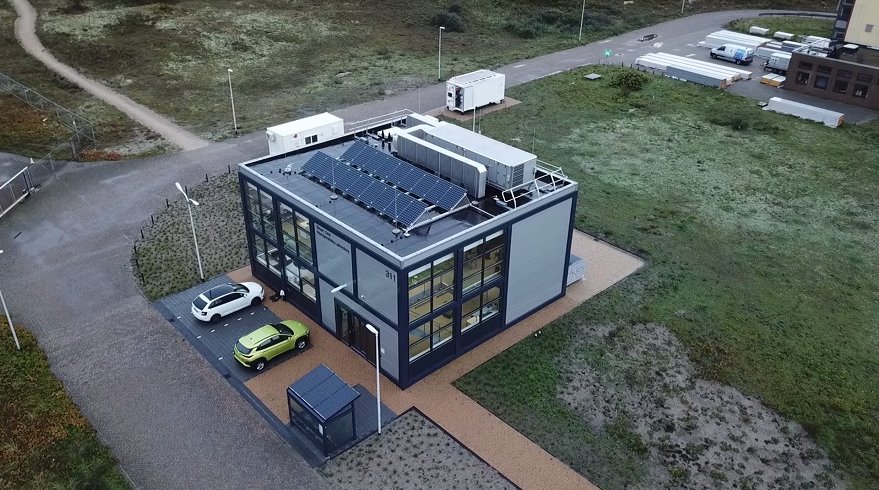
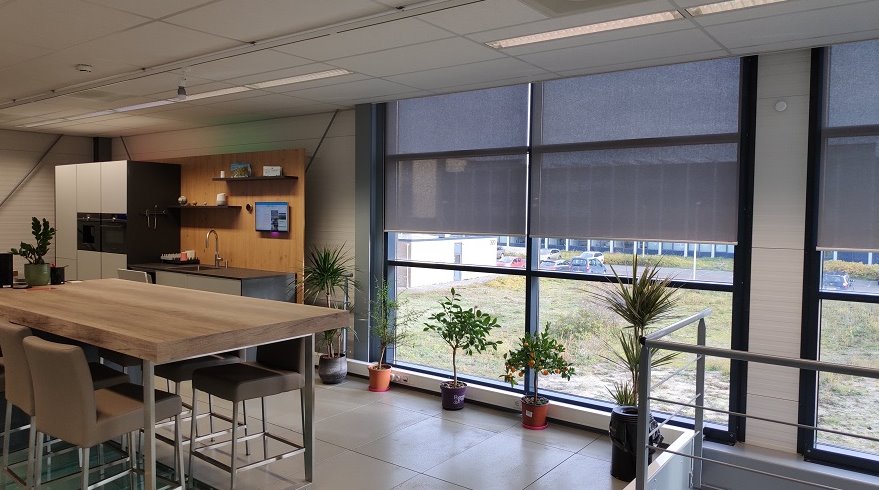
A clever laboratory for smart homes
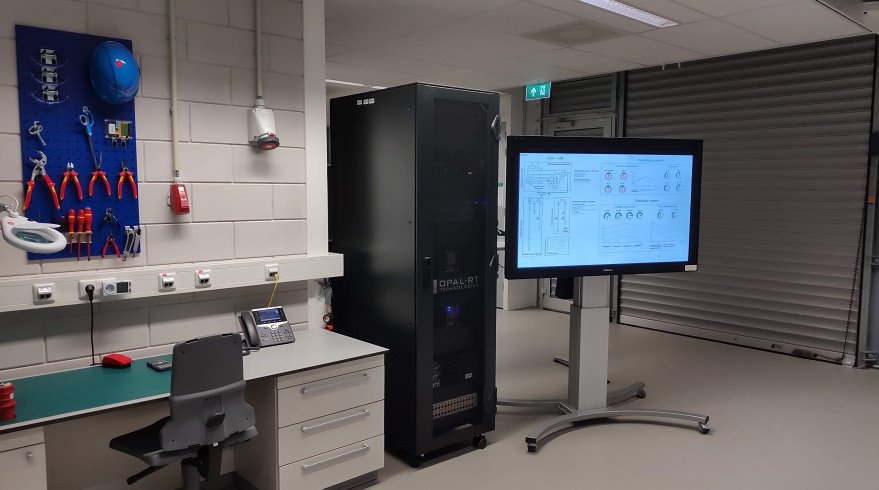
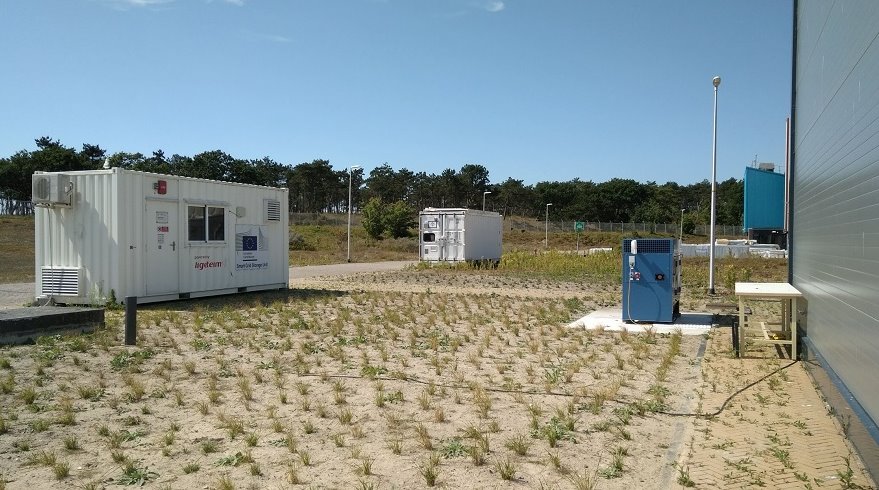
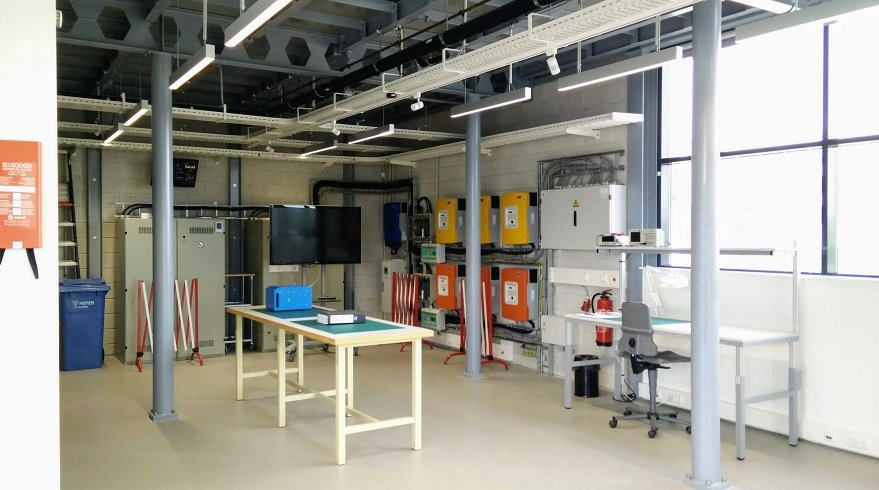
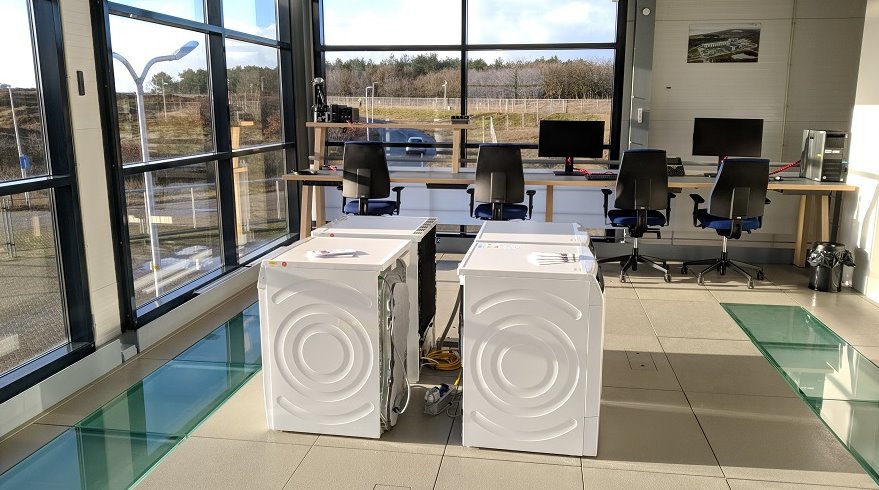
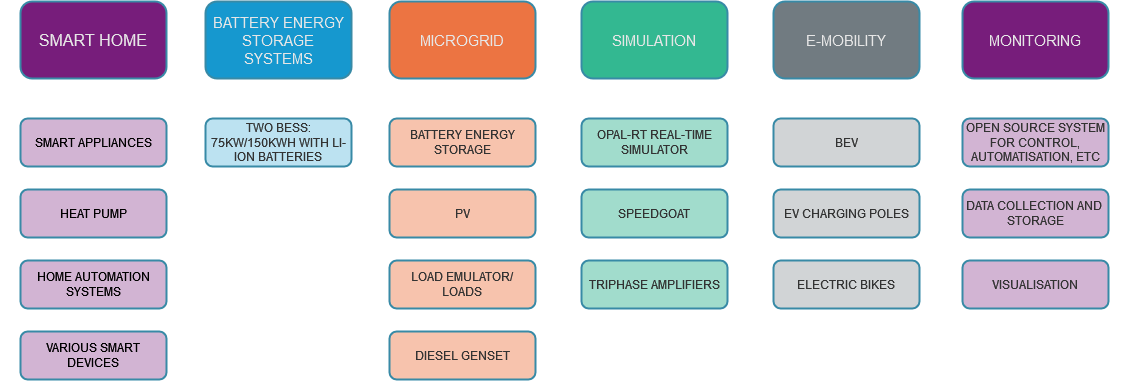
Equipment of Laboratory in Petten
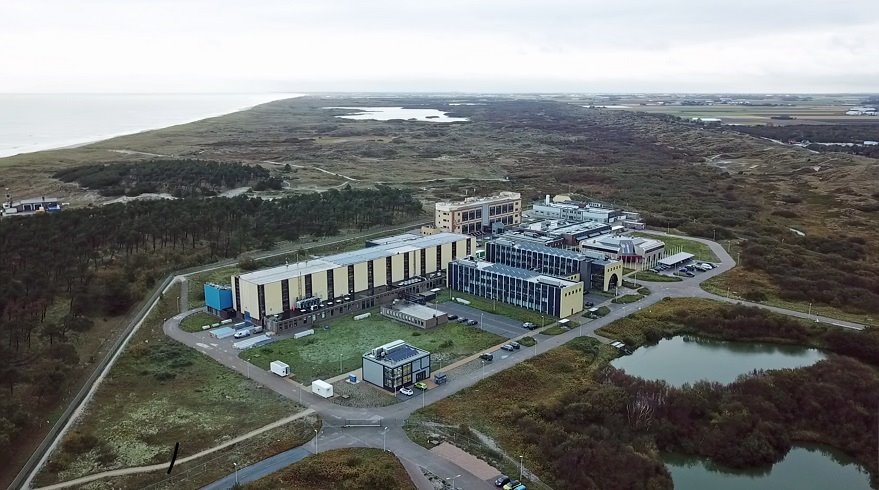
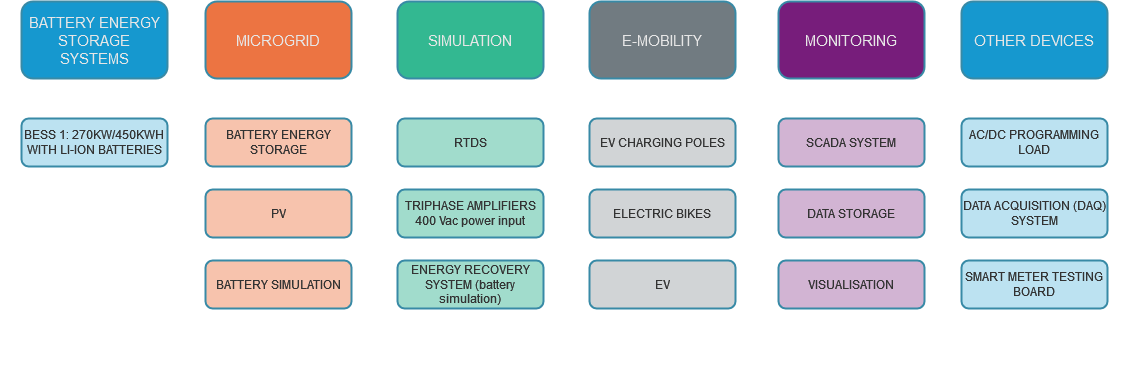
Equipment of Laboratory in Ispra
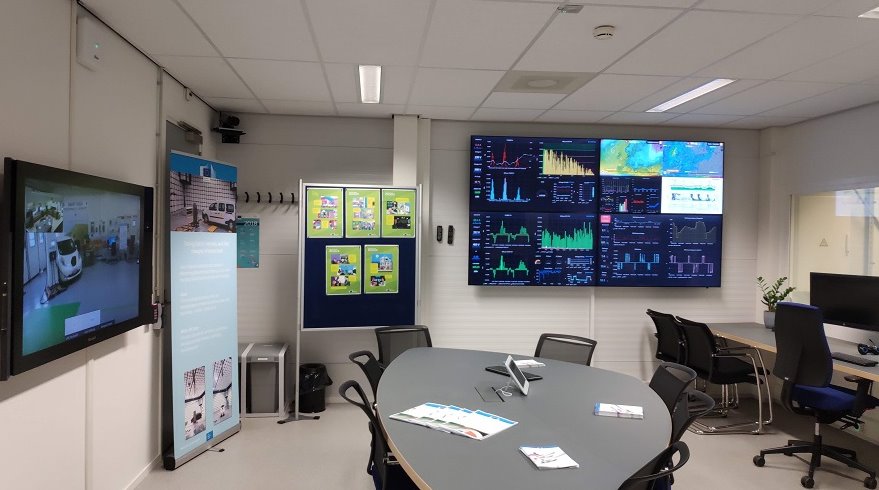
Activities & projects
Through our experimental facilities we contributed to several projects, particularly in the context of the R&I Framework Programme.
By means of the Smart Grid Interoperability Laboratory we:
- Test the interoperability of solutions, from the market and from research projects.
- Promote the use of a common interoperability testing methodology based on the CEN-CENELEC-ETSI framework.
- Network with other European laboratories and research centres for common initiatives.
- Network with European industrial actors in various sectors.
- Disseminate the results of testing campaigns.

DRIMPAC
DRIMPAC (2018 - )“Unified DR interoperability framework enabling market participation of active energy consumers” is a project funded by the EU’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under the Energy Efficiency Innovation Action. (https://www.drimpac-h2020.eu/)

ERIGrid-II
ERIGrid-II (2020-2023). European Research Infrastructure supporting Smart Energy Systems Research, Technology Development, Validation and Roll Out - Second Edition (Horizon2020 project, https://erigrid2.eu)
ERIC-LAB
ERIC-LAB (2015 - ). European Real-time Integrated Co-simulation laboratory (http://www.eric-lab.eu)

DELTA
DELTA (2018-21). Future tamper-proof Demand rEsponse framework through seLf-configured, self-opTimized and collAborative virtual distributed energy nodes (https://www.delta-h2020.eu)

AnyPLACE
AnyPLACE (2015-18). Low-cost, modular energy management system for home automation and grid services (Horizon2020 project, http://www.anyplace2020.org)
Contact
Location: Smart Grid Interoperability Laboratory (Building 18), European Commission - Joint Research Centre (JRC), Via Enrico Fermi, 2749. 21027 Ispra (VA), Italy
Tel: +39 033278-5450
Location: Smart Grid Interoperability Laboratory (Building 311), European Commission - Joint Research Centre (GCO), Westerduinweg 3 NL-1755 LE Petten
Tel: +31 (0)224 565656 (switchboard)
Postal address: European Commission - JRC/GCO P.O. Box 2, NL-1755 ZG Petten
Directions: The Joint Research Centre is situated in a research park, just north of the Petten village (20 km north of Alkmaar).








